2024年8月,国家血液系统疾病临床医学研究中心、苏州大学附属第一医院、造血干细胞移植研究所吴德沛、徐杨教授课题组在血液学Top杂志Blood(IF=21)在线发表题为“YAP1 regulates thrombopoiesis by binding to MYH9 in immune thrombocytopenia”最新研究成果,报道了Yes相关蛋白1(YAP1)通过与细胞骨架相关蛋白MYH9结合,调控巨核细胞骨架,影响血小板生成的机制。

免疫性血小板减少症(ITP)是一种由于免疫失衡引起的获得性出血性自身免疫性疾病,其特点是血小板大幅减少。尽管近年来研究逐步深入,但其复杂的发病机制仍不够明确。ITP的病理机制主要与免疫调节异常相关,表现为血小板的加速破坏和生成减少,引发皮肤、黏膜和内脏等多种组织的出血症状。作为ITP中主要的参与因素,巨核细胞负责血小板生成。然而,ITP中巨核细胞内血小板生成失调的具体机制尚未明了。
本研究探讨了在ITP中YAP1在血小板生成中的作用。首先观察到ITP患者的巨核细胞中,YAP1表达降低且伴随细胞骨架缺陷。通过实验小鼠ITP模型,我们发现YAP1表达部分缺失会引起巨核细胞髓内分布异常,降低晚期成熟巨核细胞的比例,并导致血小板恢复水平明显受限。通过分子机制探讨,证实转录因子GATA1可以结合YAP1启动子并上调YAP1基因表达,促进巨核细胞成熟。磷酸化的YAP1通过其WW2结构域与骨架相关蛋白MYH9结合,激活巨核细胞骨架,从而促进血小板生成。最后,利用YAP1激活剂XMU-MP-1对YAP1+/-ITP小鼠和患者巨核细胞进行YAP1恢复治疗,结果显示YAP1的回补可以有效逆转细胞骨架缺陷和血小板生成的失调,促进血小板生成。综上所述,YAP1在血小板生成中发挥着关键作用,为诊断和治疗提供了潜在靶点。
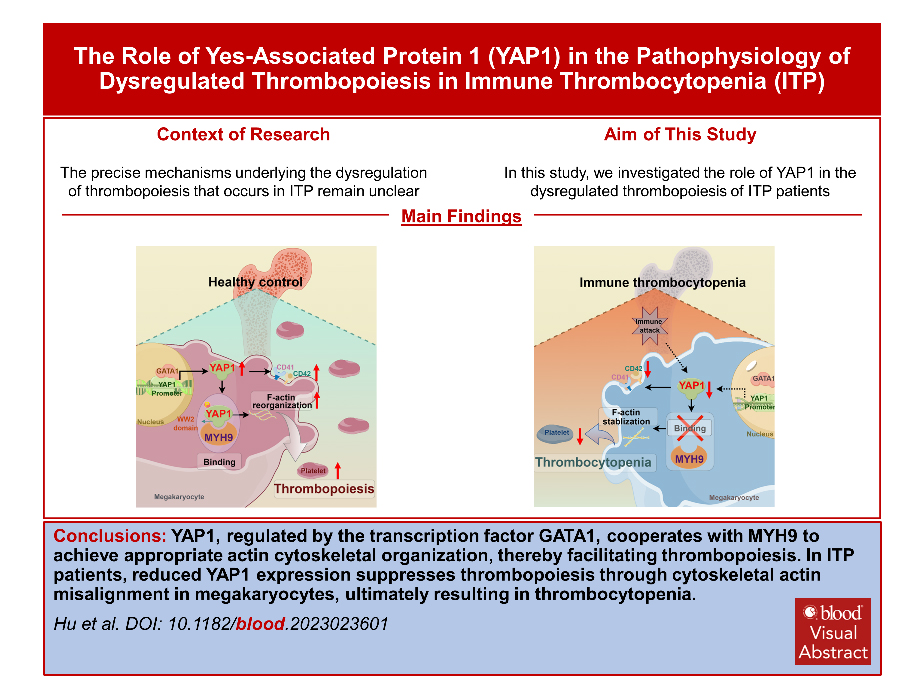
(YAP1通过与MYH9结合调控细胞骨架参与ITP发病机制的模式图)
国家血液系统疾病临床医学研究中心、苏州大学附属第一医院、苏州大学造血干细胞移植研究所吴德沛教授、徐杨教授为本文的共同通讯作者。胡淑鸿、刘艺飞为本文共同第一作者。该研究得到国家自然科学基金委、科技部、国家血液系统疾病临床医学研究中心、江苏省科技厅等多个科研资金的支持。
原文摘要:Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a complicated bleeding disease characterized by sharp platelet reduction. As a dominating element involved in ITP, megakaryocytes (MKs) are responsible for thrombopoiesis. However, the mechanism underlying the dysregulation of thrombopoiesis that occurs in ITP remains unidentified. In this study, we examined the role of yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) in thrombopoiesis during ITP. We observed a reduced YAP1 expression with cytoskeletal actin misalignment in MKs from ITP patients. By using an experimental ITP mouse model, we showed that reduced YAP1 expression induced aberrant MK distribution, reduced the percentage of late MKs among total MKs, and caused submaximal platelet recovery. Mechanistically, YAP1 upregulation by binding of GATA binding protein 1 (GATA1) to its promoter promoted MK maturation. Phosphorylated YAP1 promoted cytoskeletal activation by binding of its WW2 domain to myosin heavy chain 9 (MYH9), facilitating thrombopoiesis. Targeting YAP1 by its activator XMU-MP-1 was sufficient to rescue cytoskeletal defects and thrombopoiesis dysregulation in YAP1+/- mice with ITP and patients. Taken together, these results demonstrate a crucial role for YAP1 in thrombopoiesis, providing a potential for the development of diagnostic markers and therapeutic options for ITP.
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2023023601